Are you ready to unlock the full potential of your connected devices? The future of device management is here, and it's all about IoT remote monitoring and control. It's no longer sufficient to simply connect devices; the real power lies in the ability to manage, monitor, and control them from anywhere in the world. This capability is rapidly transforming industries and redefining how we interact with technology, both at home and in the workplace.
That's where IoT remote monitoring truly shines. We are moving beyond the rudimentary control methods of the past. The year 2024 marks a significant shift, as traditional mobile or web applications and simple voice assistant integrations are no longer the only avenues for managing and monitoring the ever-expanding universe of IoT devices. Todays consumers, device end users, and industrial IoT equipment operators are demanding and expecting a wider range of options to interact seamlessly with their connected devices. They are looking for intuitive, efficient, and secure ways to oversee operations, troubleshoot issues, and optimize performance, regardless of location.
Consider the possibilities: Imagine a farmer using IoT sensors to monitor soil conditions and remotely control irrigation systems in a greenhouse, optimizing water usage and maximizing crop yields. Think of a factory manager overseeing the performance of hundreds of machines from a single dashboard, identifying potential problems before they lead to costly downtime. Picture a homeowner adjusting the temperature and lighting in their house from a thousand miles away, ensuring comfort and energy efficiency. These are just a few examples of the transformative power of IoT remote monitoring and control.
- Remoteiot On Windows 10 Free Access Manage Iot Devices
- Warning Evan Kate Scam Exposed Dont Fall For It
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| IoT Remote Monitoring | Technology enabling the observation and supervision of devices and systems from a distance using IoT sensors and connectivity. |
| IoT Remote Control | The ability to manage and operate devices and systems from a remote location through a network. |
| Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) | Measurable values that demonstrate how effectively a company is achieving key business objectives, such as energy efficiency and water usage. |
| Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) | Networks of spatially distributed sensor nodes that monitor physical or environmental conditions and transmit data wirelessly. |
| Fuzzy Logic | A form of many-valued logic in which the truth values of variables may be any real number between 0 and 1, allowing for degrees of truth and uncertainty. |
| 5G Wireless Networks | The fifth generation of wireless technology, offering faster speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity compared to previous generations. |
| Data Acquisition Layer | The layer of a system responsible for collecting data from sensors and other sources. |
| Communication Network Layer | The layer that handles the transmission of data between different components of a system. |
| Application Layer | The layer that provides the interface for users to interact with the system and access data. |
| Particle IoT Device Management Interface | A platform for managing and controlling Particle IoT devices, allowing for remote commands and software updates. |
| Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) | A technology that allows monitoring and control of devices and systems from a remote location, often used in IT management. |
A comprehensive guide reveals the top 20 ways to manage and control IoT devices, offering a roadmap for businesses and individuals seeking to leverage the power of remote access. These methods encompass a wide range of technologies and approaches, from sophisticated cloud-based platforms to innovative edge computing solutions. The common thread is the ability to interact with devices in real-time, analyze data, and make informed decisions that drive efficiency and productivity.
One compelling example of the power of IoT remote monitoring and control lies in the realm of smart agriculture. By deploying a system that integrates IoT and wireless sensor networks (WSN), farmers can remotely monitor and control greenhouse environments. This capability directly contributes to the core key performance indicators (KPIs) of remote monitoring and control. Imagine a farmer able to precisely adjust temperature, humidity, and lighting levels, creating the optimal conditions for plant growth, all from a remote location.
Furthermore, the implementation of a fusion and decision system, often based on fuzzy logic, can significantly enhance the performance of these systems. Fuzzy logic allows for more nuanced and flexible control, enabling the system to adapt to changing conditions and optimize resource allocation. This approach directly contributes to key performance indicators such as energy efficiency and water usage, ensuring that resources are used wisely and sustainably. The ability to remotely monitor these factors and adjust settings accordingly is a game-changer for the agricultural industry, promoting both economic and environmental benefits.
- Best Free Android Apps For Iot Device Remote Ssh Access
- Secure Remote Access Best Ssh Solutions For Iot Devices
An IoT-based remote monitoring system enables a level of control and oversight that was previously unattainable. A research paper detailed a method for controlling remote monitoring of a solar photovoltaics system using the Internet of Things (IoT). This illustrates the versatility of the technology, demonstrating its applicability across diverse sectors. The ability to monitor the performance of solar panels remotely, identify potential issues, and optimize energy production is crucial for maximizing the efficiency and reliability of renewable energy sources.
To illustrate the practical implementation of IoT remote monitoring and control, consider the use of specific technologies available as a service to demonstrate the proposed architecture on an automated electric induction motor use case. This demonstrates the power and flexibility of IoT in an industrial setting. By leveraging cloud-based platforms and readily available tools, businesses can quickly and easily implement remote monitoring and control solutions, without the need for significant upfront investment in hardware and software.
The architecture of a typical IoT remote monitoring and control system consists of several key layers: the power layer, the data acquisition layer, the communication network layer, and the application layer. The power layer provides the necessary energy to power the devices and sensors. The data acquisition layer is responsible for collecting data from the sensors and converting it into a digital format. The communication network layer transmits the data to a central server or cloud platform. And the application layer provides the user interface and tools for analyzing and visualizing the data, as well as controlling the devices.
A well-designed platform allows for comprehensive data collection related to energy consumption, data storage, and visualization. This data-driven approach empowers users to make informed decisions, optimize performance, and identify areas for improvement. The ability to track energy usage in real-time, analyze trends, and identify potential inefficiencies is crucial for businesses seeking to reduce costs and minimize their environmental impact.
The rapid development of 5G wireless networks and modern data transmission protocols is creating even greater opportunities for advancement in this field. 5G offers faster speeds, lower latency, and greater bandwidth compared to previous generations of wireless technology. This enables more reliable and responsive remote monitoring and control, as well as the ability to transmit larger amounts of data in real-time. The combination of IoT and 5G is poised to revolutionize industries ranging from manufacturing to healthcare to transportation.
An overview of monitoring and control systems based on the Internet of Things highlights the diverse applications and potential benefits of this technology. From smart homes to smart cities, IoT is transforming the way we live and work. The ability to remotely monitor and control devices and systems is enabling greater efficiency, productivity, and convenience.
The authors delve into various aspects of these systems, exploring the challenges and opportunities associated with their implementation. These include issues such as security, privacy, and scalability. Addressing these challenges is crucial for ensuring the widespread adoption and long-term success of IoT remote monitoring and control.
Imagine being able to control your remote products from anywhere in the world. This is the promise of IoT, and it's becoming a reality for more and more businesses and individuals. Whether it's monitoring air quality, controlling smart home products, or managing garage sensors, the possibilities are endless.
With the Particle IoT device management interface and cloud APIs, users can send commands and new software updates to their devices with a simple click of a button. This streamlined approach simplifies the management of large deployments of IoT devices, making it easier to keep them up-to-date and secure. The ability to remotely update software and firmware is particularly important for addressing security vulnerabilities and ensuring the continued performance of devices.
IoT remote control is exceedingly valuable across the board in all industries. It is a powerful mechanism to remotely control IoT, offering unparalleled flexibility and efficiency. From monitoring critical infrastructure to managing industrial equipment, the benefits of remote control are undeniable.
Adhering to 5 best practices for secure and efficient IoT remote control is paramount. These practices include implementing strong security measures, using secure communication protocols, regularly updating software and firmware, monitoring device activity, and implementing robust access controls. By following these guidelines, businesses can minimize the risk of security breaches and ensure the reliable operation of their IoT systems.
Remote monitoring IoT, also known as remote monitoring and management (RMM), is a technology that enables the monitoring and control of devices and systems from a remote location through the use of IoT sensors and connectivity. RMM is widely used in IT management to monitor the health and performance of computer systems and networks. However, its principles can be applied to a wide range of other applications, including industrial automation, healthcare, and agriculture.
Combining remote control functionalities with monitoring capabilities creates a powerful synergy. This allows users to not only observe the state of their devices and systems, but also to take corrective action when necessary. The ability to remotely diagnose and resolve issues can save time and money, and improve the overall reliability of systems.
Gaining a complete overview of all IoT devices in a single dashboard is crucial for effective management. This provides a centralized view of the entire IoT ecosystem, allowing users to quickly identify potential problems and track performance trends. A well-designed dashboard should provide real-time data, customizable alerts, and intuitive navigation.
Remotely monitor CPU, memory and network usage, receive alerts based on monitored IoT data and run batch jobs on devices. This level of granular control is essential for optimizing performance and ensuring the reliability of IoT systems. By monitoring key metrics and setting up alerts, users can proactively identify and address potential issues before they lead to significant problems.
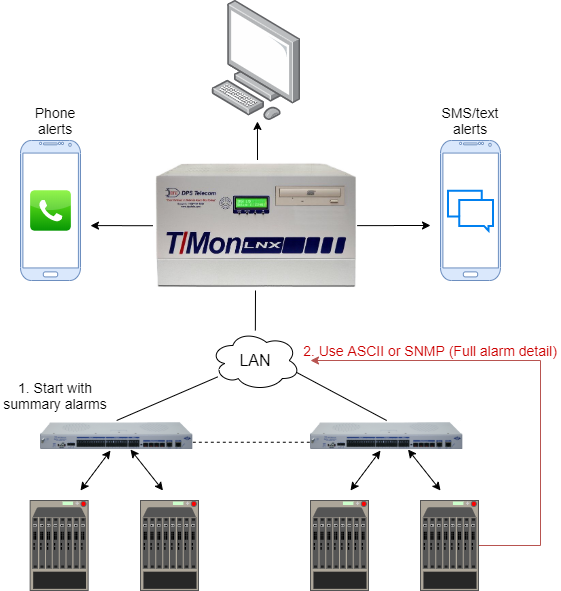

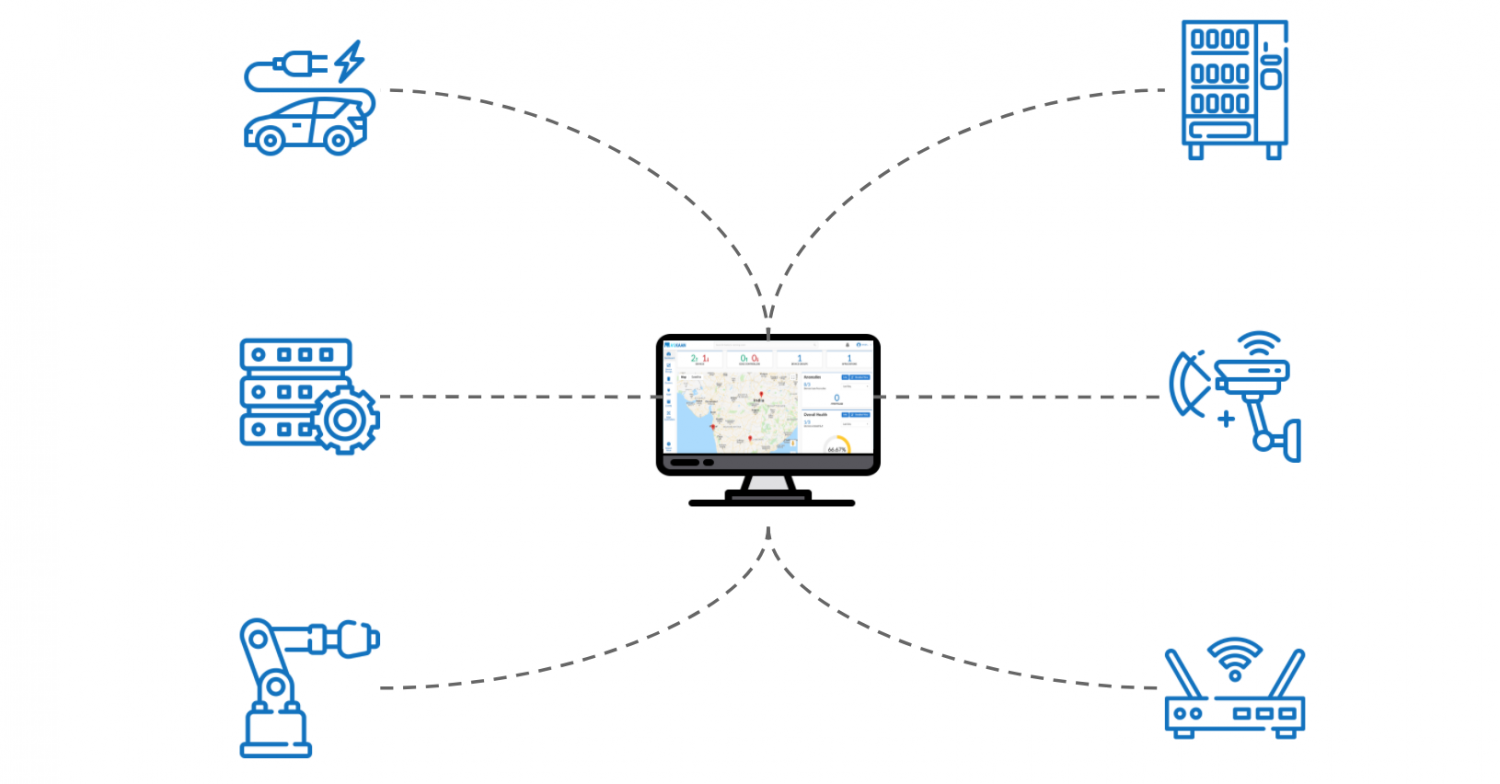
Detail Author:
- Name : Ike Towne
- Username : zwunsch
- Email : hintz.margarett@yahoo.com
- Birthdate : 1976-10-28
- Address : 124 Farrell Lane Apt. 597 East Harryside, AR 74871-8450
- Phone : +1 (520) 989-8008
- Company : Thompson, McGlynn and Jacobi
- Job : Title Examiner
- Bio : Sunt ut eligendi eos. Autem ut excepturi et veritatis quo. Quos voluptatem cum rerum unde. Non quia eum quia sapiente laudantium.
Socials
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/abernathy1988
- username : abernathy1988
- bio : Sit vel eum amet nihil odio reiciendis et.
- followers : 2524
- following : 867
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/jerry_abernathy
- username : jerry_abernathy
- bio : Omnis autem et illo eum facere. Consequatur modi ut quas odio harum quos. Omnis saepe tenetur dolore et distinctio quod.
- followers : 5421
- following : 2399
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/jerry3646
- username : jerry3646
- bio : Consequatur suscipit laboriosam odio.
- followers : 6905
- following : 1257